difference between cauda equina and conus medullaris|cauda equina versus conus medullaris : Baguio The conus medullaris (medullary cone) is the cone-shaped terminal portion of the spinal cord.The tip of the conus medullaris is found between the L1 and L2 vertebra in the average adult. The . Profissionalismo, qualidade e eficiência. Estamos prontos par.
0 · where does conus medullaris end
1 · where does cauda equina end
2 · conus vs cauda equina syndrome
3 · conus medullaris terminates at t12
4 · conus medullaris and filum terminale
5 · cauda equina vs medullaris
6 · cauda equina versus conus medullaris
7 · cauda equina and filum terminale
Resultado da A guia de jogos do Guinea mostra as últimas 100 partidas de futebol com estatísticas e ícones de vitória/empate/derrota. Há também todas as partidas que o Guinea jogará no futuro. O gráfico de desempenho e forma do Guinea é um algoritmo exclusivo do Sofascore que geramos a partir das últimas 10 .
difference between cauda equina and conus medullaris*******Cauda equina and conus medullaris syndromes have overlap in anatomy and clinical presentation. Therefore, for the purpose of this discussion, they will be grouped, and notable differences highlighted. The conus medullaris is the terminal end of the .
Cauda equina and conus medullaris syndromes have overlap in anatomy and .
The conus medullaris (medullary cone) is the cone-shaped terminal portion of the spinal cord.The tip of the conus medullaris is found between the L1 and L2 vertebra in the average adult. The .
The chart below compares and contrasts Conus Medullaris Syndrome and Cauda Equina Syndrome to showcase some of the key differences: There are many causes. The most .
Cauda equina and conus medullaris syndromes have overlap in anatomy and clinical presentation. Therefore, for the purpose of this discussion, they will be .
Multiple conditions can result in cauda equina or conus medullaris syndrome. The prognosis improves if a definitive cause is identified and appropriate treatment occurs early in the course. . An .
Cauda equina syndrome is a medical emergency that happens when an injury or herniated disk compresses nerve roots at the bottom of your spinal cord. The .
The cauda equina nerves travel down from the spinal cord. A group of nerve roots that travel down from the spinal cord and the conus medullaris is called the cauda equina. . An experimental study on the pig cauda equina with special reference to differences in effects between rapid and slow onset of compression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976 . Hunt GE Jr, Vaccaro AR. Conus .Reviewed/Revised Feb 2023. Cauda equina syndrome occurs when the nerve roots at the caudal end of the cord are compressed or damaged, disrupting motor and sensory . Trauma (even chiropractic manipulation reported rarely). Infection. Ischemia (aortic aneurysm). Main difference between Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) or Conus . Cauda equina and conus medullaris syndromes have overlap in anatomy and clinical presentation. Therefore, for the purpose of this discussion, they will be grouped, and notable differences highlighted. The conus medullaris is the terminal end of the spinal cord, which typically occurs at the L1 vertebral level in the average adult. Conus and cauda equina tumors represent a unique group of tumors due to their specific location in the spinal canal. The conus medullaris forms the last portion of the spinal cord from where the .
Trauma (even chiropractic manipulation reported rarely). Infection. Ischemia (aortic aneurysm). Main difference between Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) or Conus Medullaris Syndrome (CMS) is a more symmetrical distribution of sensory and motor deficits with CMS. CMS can give Upper Motor Neuron signs such as spasticity and . The spinal nerves S3-S5 originate in the conus and provide motor and sensory innervation to the lower extremities, bowel, bladder, and perineum. They are also crucial for sexual function. Spinal nerves L2-L5, S1-S5, and Co1 continue inferiorly as the cauda equina. Compression of these nerves can produce cauda equina or conus . the differences between them in order to deal with any case promptly and accurately. . For cauda equina/conus medullaris lesions an annual incidence rate of 3.4/1.5 per million, and period .
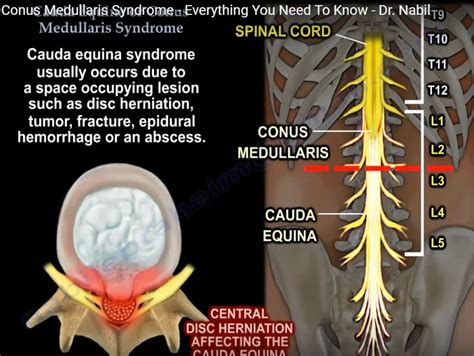
The cauda equina is the sack of nerve roots (nerves that leave the spinal cord between spaces in the bones of the spine to connect to other parts of the body) at the lower end of the spinal cord. These nerve roots provide the ability to move and feel sensation in the legs and the bladder.
difference between cauda equina and conus medullaris cauda equina versus conus medullarisThe cauda equina is the sack of nerve roots (nerves that leave the spinal cord between spaces in the bones of the spine to connect to other parts of the body) at the lower end of the spinal cord. These nerve roots provide the ability to move and feel sensation in the legs and the bladder.cauda equina versus conus medullarisConus medullaris, filum terminale and cauda equina The spinal cord ends at the level of the first or second lumbar vertebrae (L1 / L2) as a cone-shaped termination called the conus medullaris (medullary cone). It consists of the sacral and coccygeal spinal cord segments (S2 - Co1 segments). Check it out. Previous slide 5 / 19 . This document discusses conus medullaris syndrome and cauda equina syndrome, two conditions that result from compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots in the lower back. It describes the differences in presentation and symptoms between the two syndromes. Specifically, conus medullaris syndrome affects the sacral cord .
Video describes anatomical & clinical difference between conus medullaris & cauda equina lesions. For similar educational videos in Neurology please download.Cauda equina syndrome (like conus medullaris syndrome) causes distal leg paresis and sensory loss in the distribution of the affected nerve roots (often in the saddle area), as well as bladder, bowel, and pudendal dysfunction (eg, urinary retention, urinary frequency, urinary or fecal incontinence, erectile dysfunction, loss of rectal tone, abnormal .

Conus medullaris syndrome (CMS) and cauda equina syndrome (CES) are well-known neurological entities. It is assumed that these syndromes are different regarding neurological and functional prognosis. In cauda equina syndrome, saddle hypo/anaesthesia occurs. Mnemonic: Conus rhymes with anus for perianal anaesthesia. Cauda equina syndrome is usually asymmetric. Conus medullaris is symmetric. Mnemonic: cAudA has A's for Asymmetric involvement. Conus medullaris has early onset of bowel and bladder involvement. CES .
Oxford Online Practice is an online course component for En.
difference between cauda equina and conus medullaris|cauda equina versus conus medullaris